By Sue Petersen, Clinical Nutritionist | Health Simple

What Is Aspirin?
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It works by blocking an enzyme called COX-1, which plays a key role in producing prostaglandins—compounds that trigger inflammation, pain, fever, and help platelets stick together to form clots.
In one sentence? Aspirin reduces pain, inflammation, and clot formation by turning off your body’s chemical messengers.
Why Is Aspirin Used for the Heart?
Low-dose aspirin (typically 81 mg) is widely recommended for people who have had a heart attack or stroke, or who are at high risk for cardiovascular events. It thins the blood by reducing platelet stickiness, making it harder for clots to form and block arteries.
However—this is a big one—aspirin is no longer recommended for routine prevention in healthy older adults. Why? Because the risk of bleeding may outweigh the benefit in people without a history of heart disease.
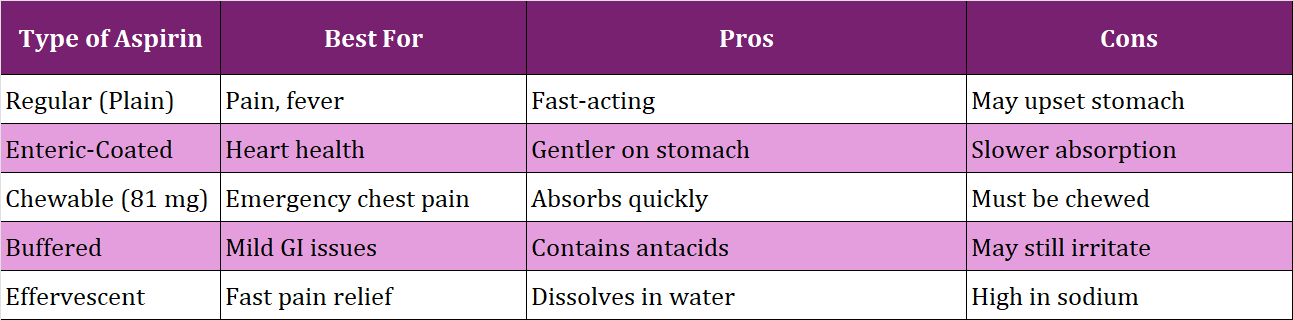
Are All Aspirin Products the Same?
Not quite. While the active ingredient is the same, the way it's formulated and absorbed can vary. Here's a quick guide:
Aspirin Product Comparison
Nutrition Matters: Aspirin and Nutrient Depletion
What many don’t realize is that long-term aspirin use can deplete key nutrients:

Aspirin Isn’t a Free Pass
It's tempting to rely on a pill to protect your heart, but aspirin doesn’t replace lifestyle. In fact, your plate may be more powerful than your pillbox.
Here’s what supports long-term vascular health:
• Mediterranean-style diet (rich in olive oil, greens, and omega-3s)
• Daily movement
• Restorative sleep
• Stress management
• No smoking
What Herbs are aspirin “like”?
Bottom Line
Aspirin can be a life-saving medication when used correctly—but it's not for everyone. The form you choose matters. The timing matters. And your whole-body health matters most.
Before starting or continuing aspirin, ask:
• Why am I taking this?
• What form is right for me?
• What can I do nutritionally to support my body better?
Your heart deserves more than a pill—it deserves a whole approach. 💛
Herbs that are "aspirin-like" share similar anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), antipyretic (fever-reducing), or antiplatelet (blood-thinning) properties to aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Many of these herbs contain salicylates or compounds that act on the COX (cyclooxygenase) pathway, much like aspirin.

Here's a list of aspirin-like herbs, their key compounds, and typical actions:
🌿 1. White Willow Bark (Salix alba)
Aspirin-like Compound: Salicin → converted to salicylic acid in the body.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic.
Notes: Known as the original source of aspirin. Slower onset but longer duration of action.
🌿 2. Meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria)
Aspirin-like Compound: Salicylaldehyde, salicylic acid.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving, stomach-protective.
Notes: Contains tannins and mucilage that may buffer stomach lining (unlike aspirin).
🌿 3. Wintergreen (Gaultheria procumbens)
Aspirin-like Compound: Methyl salicylate (a potent salicylate).
Actions: Topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Caution: Can be toxic if ingested in large amounts due to concentrated methyl salicylate.
🌿 4. Poplar Bark (Populus spp.)
Aspirin-like Compound: Salicin.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Traditional Use: Native American medicine for pain and fever.
🌿 5. Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
Aspirin-like Compound: Curcumin.
Actions: Inhibits COX-2 and NF-kB; anti-inflammatory and antioxidant.
Notes: Modulates inflammation differently than salicylates but with similar outcomes.
🌿 6. Ginger (Zingiber officinale)
Aspirin-like Compound: Gingerols, shogaols.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory, COX and LOX inhibition.
Bonus: Also good for nausea and digestion.
🌿 7. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum)
Aspirin-like Compound: Eugenol.
Actions: Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet.
Use: Often applied topically for toothaches; may thin blood in high doses.
🌿 8. Licorice Root (Glycyrrhiza glabra)
Aspirin-like Action: Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis, COX inhibition.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory, but also adaptogenic and demulcent.
Caution: Can raise blood pressure with long-term use.
🌿 9. Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium)
Aspirin-like Compound: Parthenolide.
Actions: Anti-inflammatory, platelet-inhibiting, migraine preventive.
Use: Best known for migraine and vascular headaches.
🌿 10. Devil’s Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens)
Aspirin-like Action: COX-2 inhibition.
Actions: Used for joint pain, osteoarthritis, and inflammation.
🛑 Caution:
Because some of these herbs have blood-thinning effects, they can interact with anticoagulant medications or increase bleeding risk, especially:
White willow
Wintergreen
Clove
Feverfew
Turmeric
Ginger
Want an easy-to-use downloadable Aspirin-like Herbal PDF? Click below

© 2025 Health Simple | www.SuePetersen.com

- Aug 20, 2025
Aspirin 101: What You Need to Know Before You Pop That Pill
- Sue Petersen
- 0 comments